Hot Selling Products
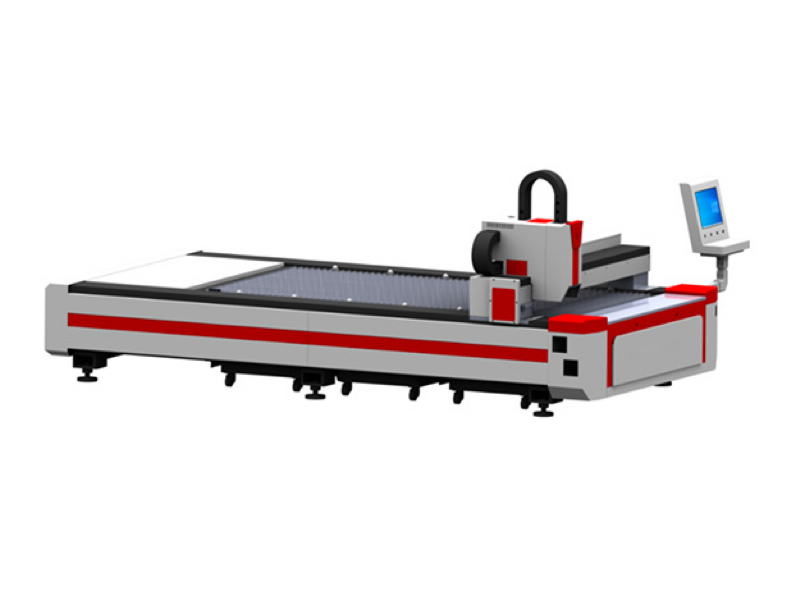
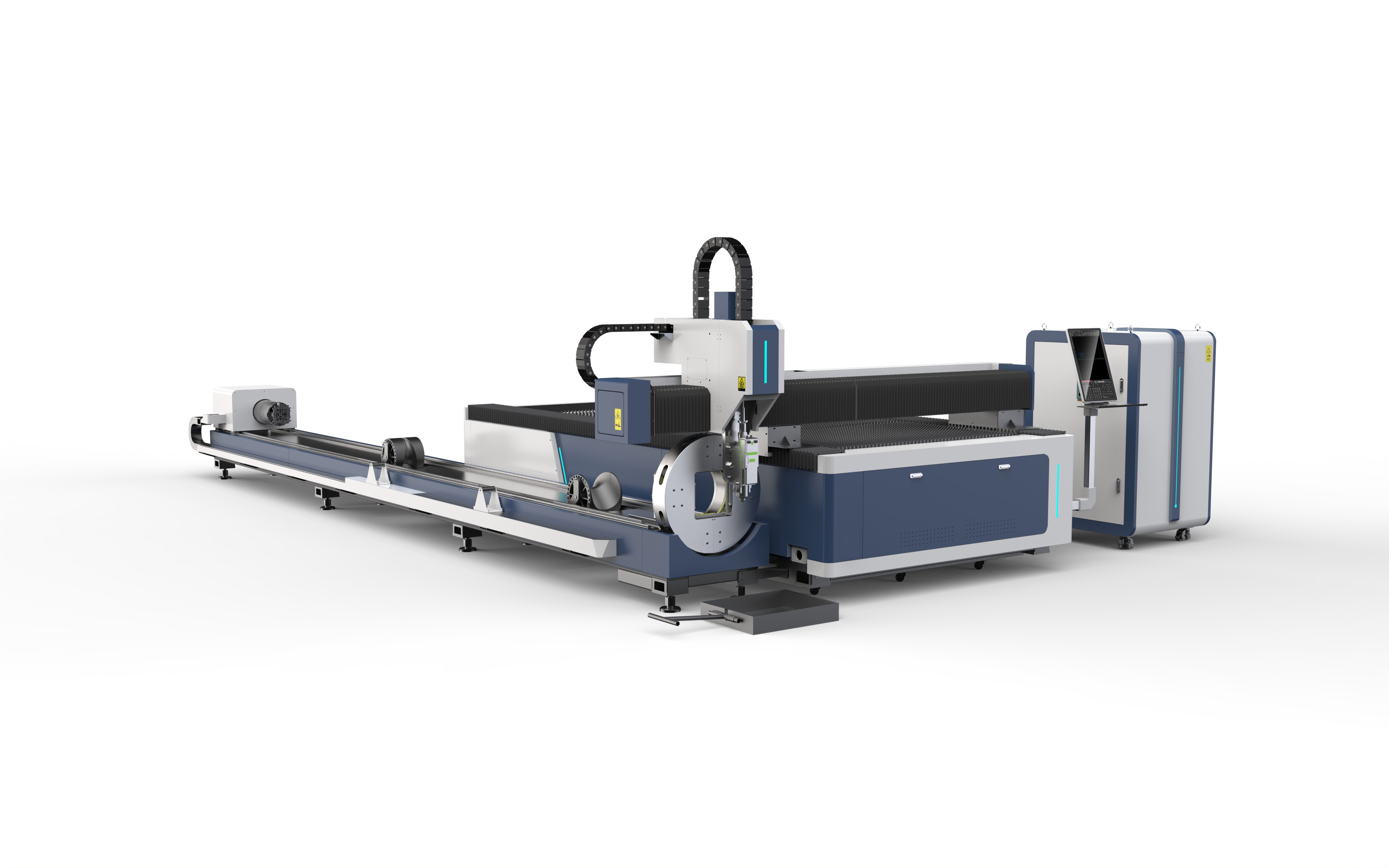
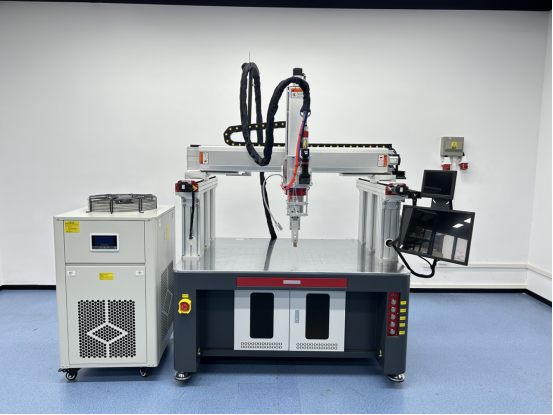
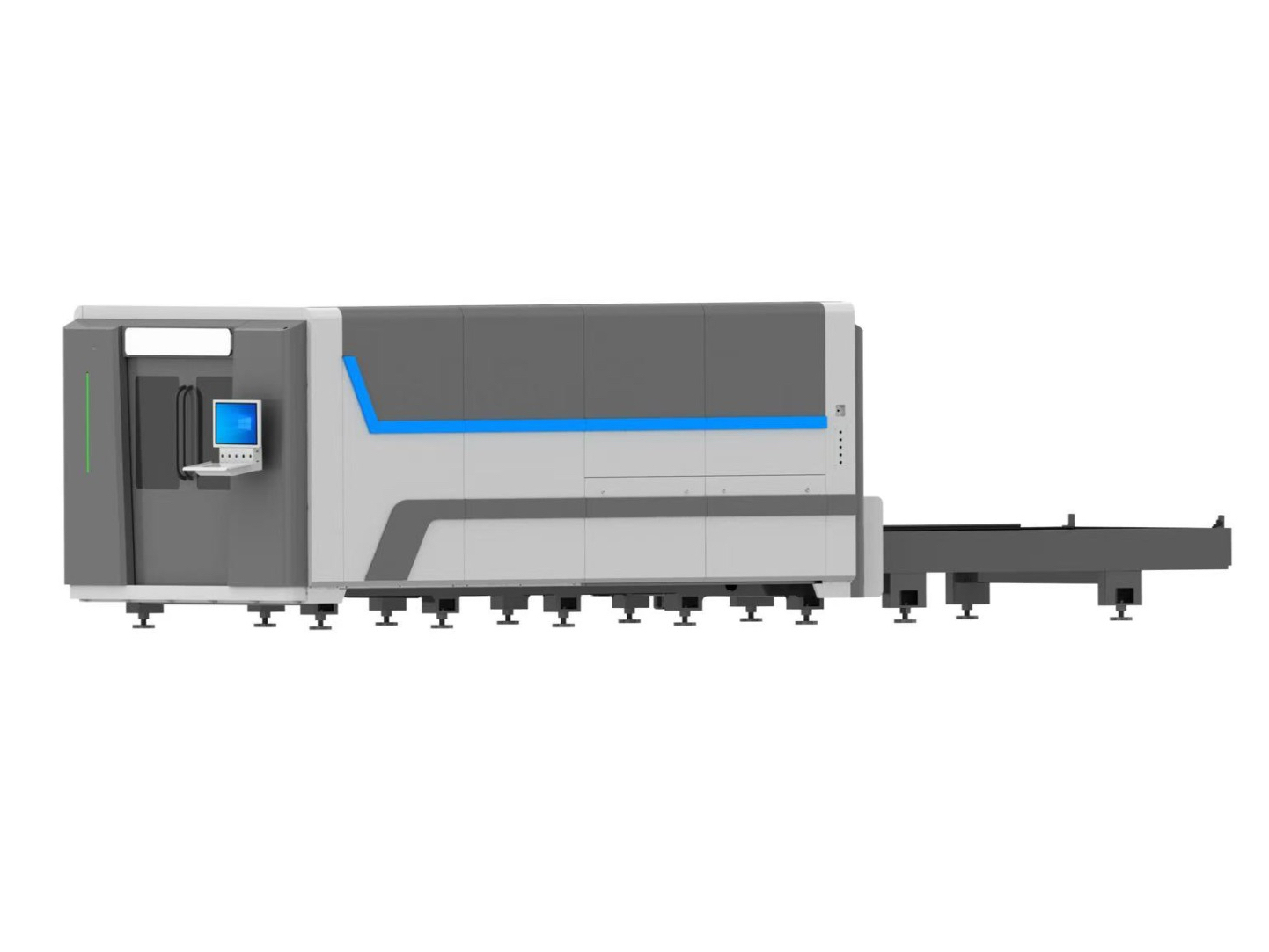
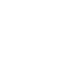
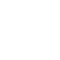
- Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
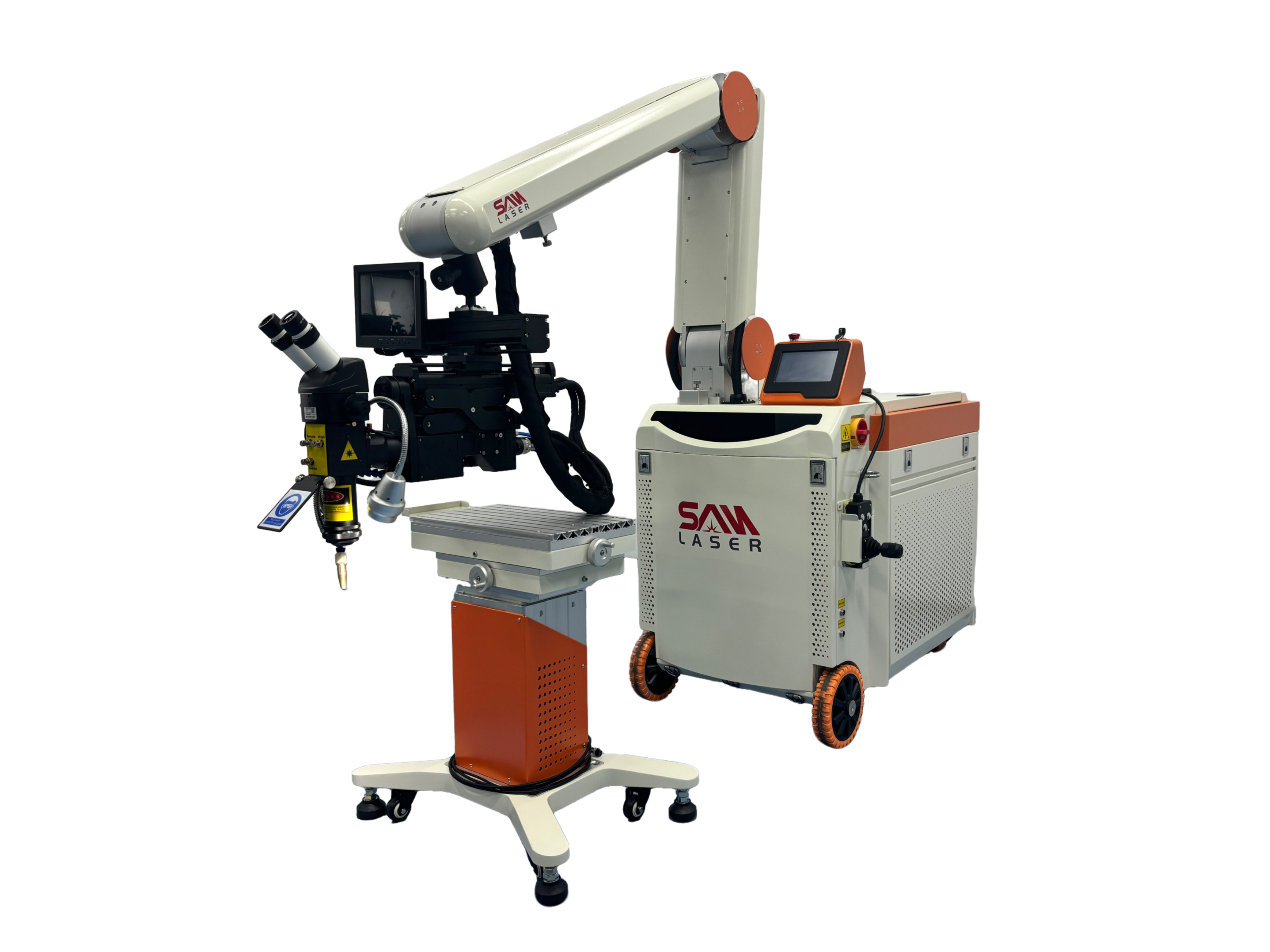
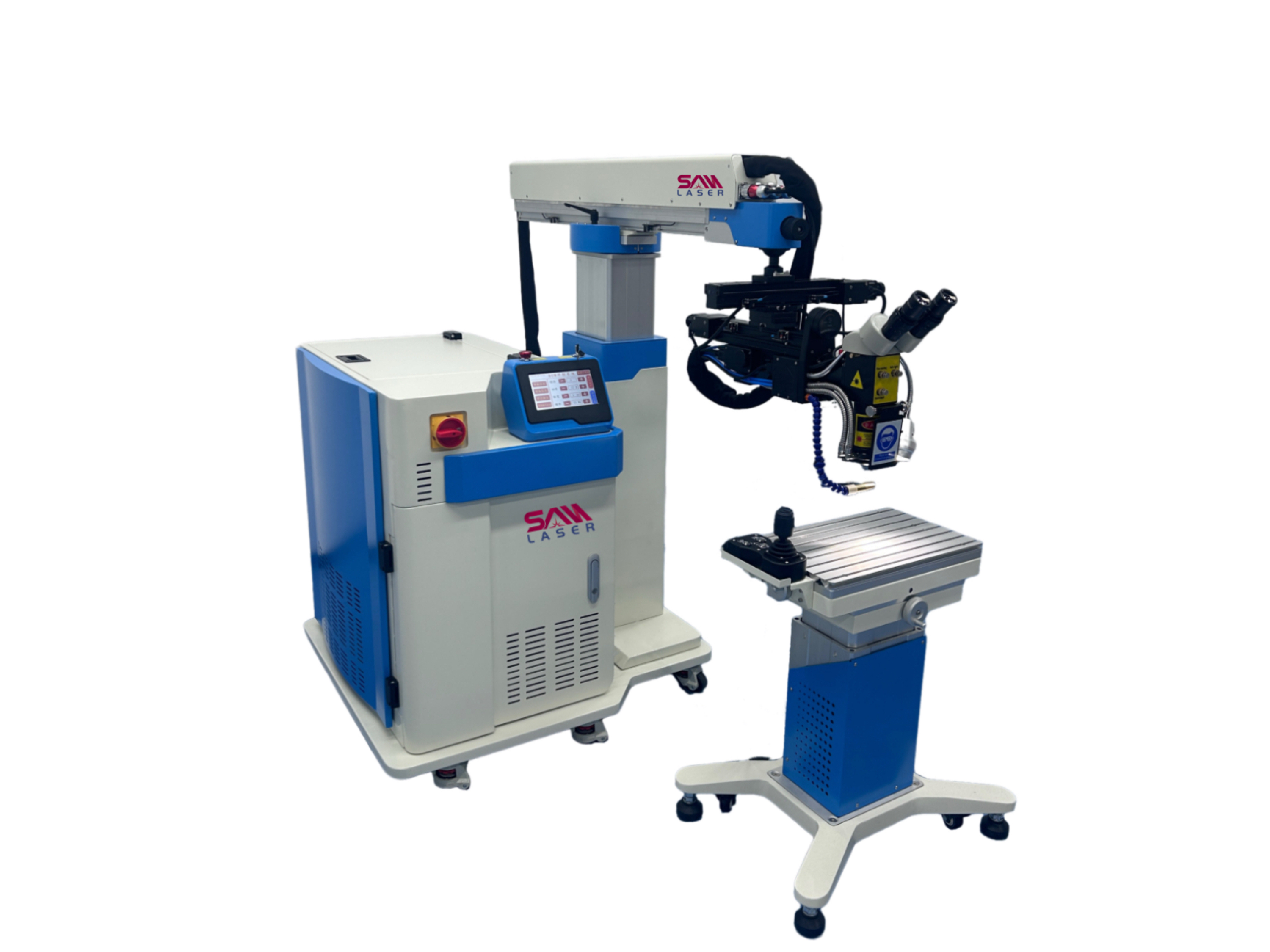
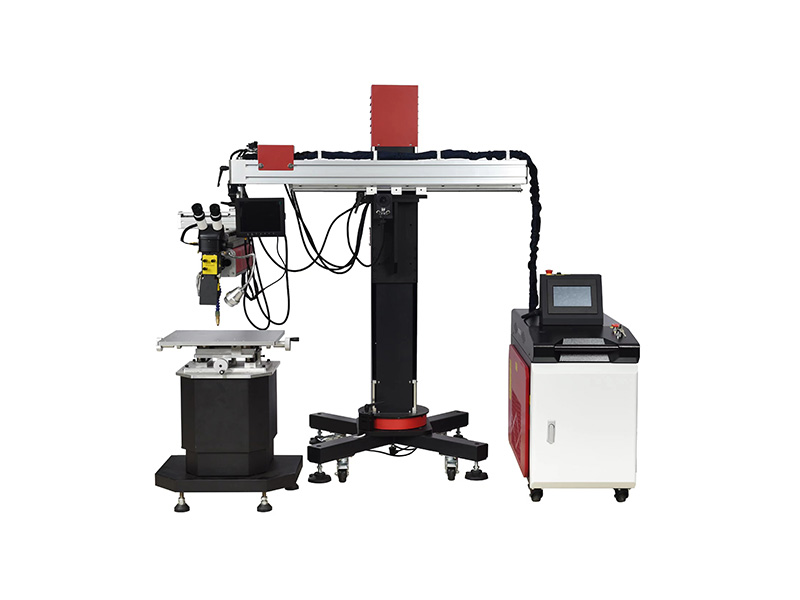
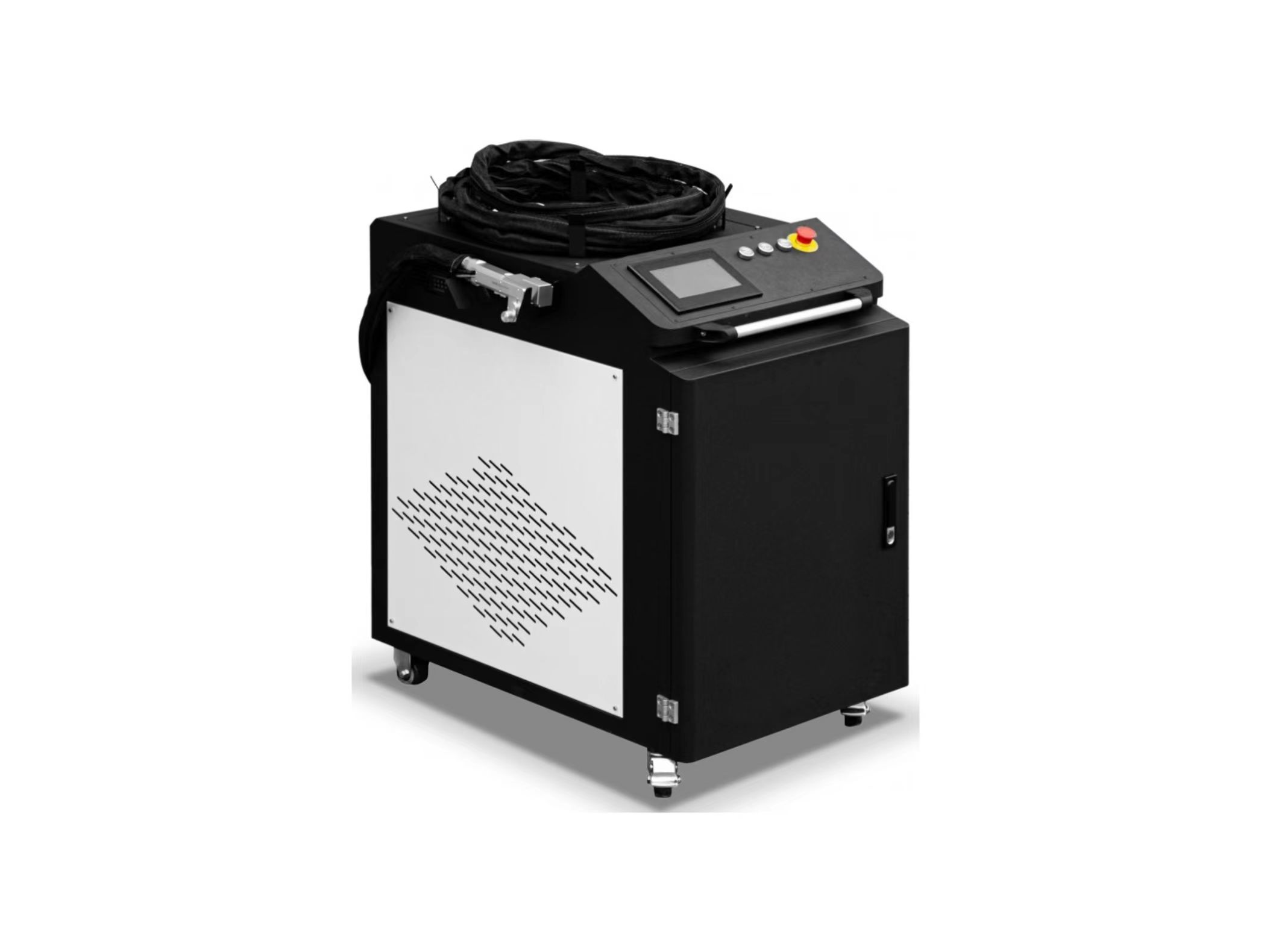
- Fiber Laser Welding Machine
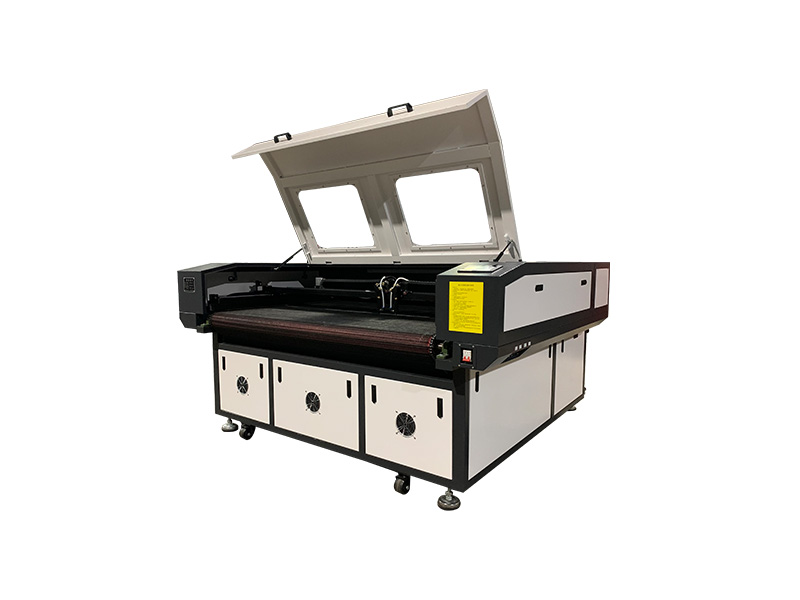
- CO2 Laser Cutting Machine
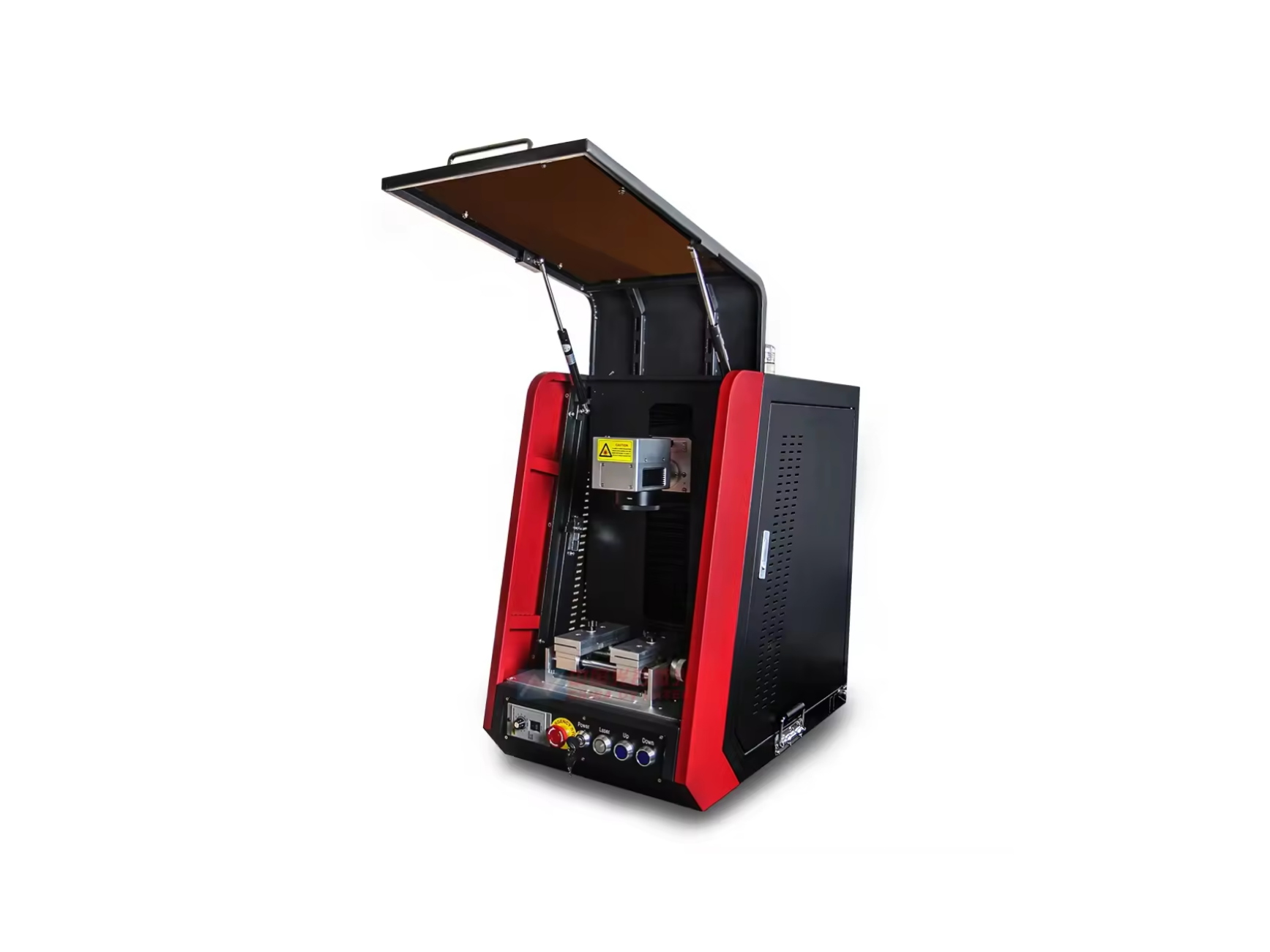
- Laser Marking Machine
core advantages
-
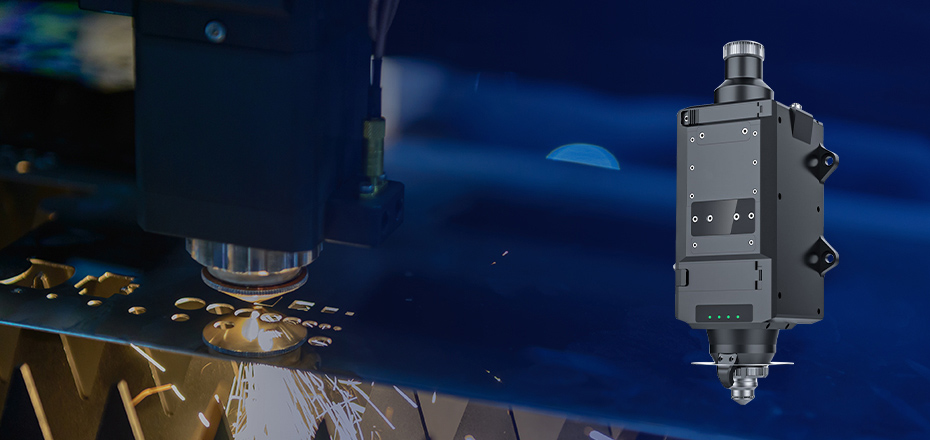 CUTTING SOLUTIONS
CUTTING SOLUTIONSFiber Laser Cutting Machine Engineering Solutions
Learn more -
 Cutting Technology
Cutting TechnologyIntelligent induction cutting head, cutting anti-collision technology
Learn more
news center
-
Apr 23,
2025Pulse Laser Cleaning vs. Fiber Laser Cleaning: Differences & RecommendationsIn the field of laser cleaning technology, two primary solutions stand out: pulse laser cleaning machines and fiber laser cleaning machines. Both technologies offer effective cleaning for various industrial applications, but their differences make them suitable for different use cases. Understanding these differences can help businesses choose the right machine for their specific needs.
Pulse Laser Cleaning Machine
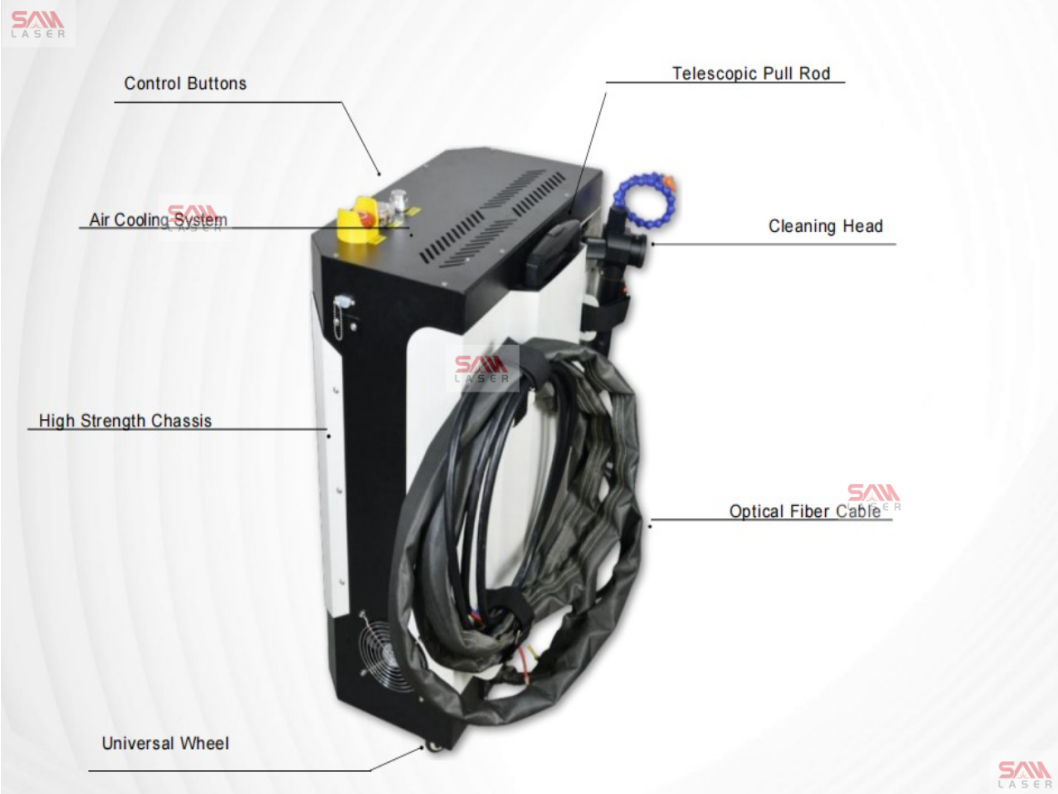

pulse laser cleaning machines utilize a solid-state laser source to generate high-energy pulses for removing rust, paint, coatings, and contaminants from surfaces. Key characteristics of pulse laser cleaning include:
Lower Cost: laser cleaning systems are generally more affordable than fiber lasers, making them a cost-effective choice for small to medium-sized businesses.
Good for Delicate Surfaces: The pulse laser operates at a lower energy density, which minimizes heat damage and makes it suitable for cleaning sensitive materials such as historical artifacts, electronics, and soft metals.
Moderate Maintenance: While lasers require periodic maintenance, they remain a reliable option for various cleaning applications.
Fiber Laser Cleaning Machine

Fiber laser cleaning machines use advanced fiber laser technology, known for its efficiency, precision, and longevity. They are widely used in industrial environments where high-speed, deep cleaning is required. Key advantages of fiber laser cleaning include:
Higher Efficiency: Fiber lasers deliver higher power and faster cleaning speeds, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications such as automotive, shipbuilding, and machinery maintenance.
Low Maintenance & Long Lifespan: Fiber laser systems have fewer consumable components and require minimal maintenance, resulting in lower operational costs over time.
Environmentally Friendly: With no chemical consumables and minimal waste, fiber laser cleaning is an eco-friendly solution that aligns with modern sustainability practices.
l Which One Should You Choose?
When selecting between YAG pulse laser cleaning and fiber laser cleaning, consider the following factors:
Budget: If cost is a primary concern, pulse laser cleaning machines may be the better choice due to their lower initial investment.
Material Sensitivity: For delicate or heat-sensitive materials, pulse laser cleaning is preferable due to its lower heat impact.
Cleaning Speed & Efficiency: If you need a high-speed, industrial-grade solution with minimal maintenance, fiber laser cleaning is the best option.
l Conclusion
Both pulse laser cleaning machines and fiber laser cleaning machines have their distinct advantages, making them suitable for different industries and applications. If you need assistance selecting the right laser cleaning machine for your business, feel free to contact us. Our team of experts is ready to provide professional guidance and recommend the best solution for your specific requirements.
For more information about our laser cleaning machines, visit our website or reach out to us directly!
Get professional support now
Related product links
-
Apr 18,
2025Market Analysis and Development Trends of Laser Mold Welding Machines (as of 2024-2025)1. Market Overview
Global Market Size: The global laser mold welding machine market was valued at approximately $1.2 billion in 2024, with a projected CAGR of 7.5% (2025-2030), driven by demand from automotive, aerospace, and precision manufacturing sectors.
Key Regions:

Asia-Pacific dominates (45% market share), led by China, Japan, and South Korea, due to rapid industrialization and mold repair needs
Europe (30%) and North America (20%) focus on high-precision applications and automation.
2. Key Applications
Mold Repair & Maintenance: Laser welding is widely used to repair high-value injection molds, die-casting molds, and stamping molds, reducing downtime and costs by 30-50%.
Automotive: Critical for welding complex mold components (e.g., engine parts, gear molds) with minimal heat distortion.
Aerospace: Used for titanium alloy and nickel-based superalloy molds requiring ultra-high precision.
Electronics: Micro-welding for semiconductor molds and precision stamping die.
3. Technological Trends
Fiber Laser Dominance: Fiber lasers (wavelength1μm) hold 65% market share due to high efficiency, compact design, and lower maintenance.
Automation Integration: Adoption of AI-driven robotic arms and real-time monitoring systems (e.g., seam tracking) improves welding accuracy by 20-30%.
Hybrid Welding: Combining laser with arc welding (e.g., laser-TIG) enhances speed and penetration for large molds.
Additive Manufacturing: Laser metal deposition (LMD) for mold surface modification and 3D printing of complex mold structure.
4. Competitive Landscape
Top Players: TRUMPF (Germany), IPG Photonics (US), Han’s Laser (China), Amada (Japan), and Coherent (US) control 60% of the high-end market.
Chinese Manufacturers: Gaining traction with cost-effective solutions (e.g., 10-30% cheaper than European counterparts), targeting emerging markets in Southeast Asia and Africa.
5. Challenges
High Initial Cost: Entry-level systems cost $50k-$100k, limiting adoption in SMEs.
Skill Gap: Requires specialized operators for parameter debugging (e.g., pulse frequency, shielding gas selection).
Material Limitations: Challenges in welding highly reflective materials (e.g., copper alloys) and ultra-thick molds (>30mm).
6. Growth Opportunities
Emerging Economies: Rising mould requirements in India, Vietnam, and Mexico due to manufacturing relocation.
Sustainability: Laser welding reduces material waste by 15-20% compared to traditional methods, aligning with ESG goals.
Customized Solutions: Demand for modular systems for niche applications (e.g., medical device molds).
Conclusion
The laser mold welding market is poised for steady growth, driven by automation, material innovation, and repair applications. Manufacturers should prioritize R&D in multi-wavelength lasers and user-friendly software to capture opportunities in Asia-Pacific and green manufacturing sectors. Collaboration with mould service providers and vocational training programs will help overcome skill barriers.
Get professional support now
Related product links
-
Apr 17,
2025Why Our Welding Machines Perfectly Adapt to the American Market? Localized Solutions for Efficient Production!In the global industrial equipment market, adapting to regional requirements is crucial. Our welding machines, with their localized design, strict certifications, and efficient service, have become the ideal choice for customers in the Americas. This article details how we optimize our equipment to fully comply with the standards and demands of the American market.

1. Compliant with Strict American Safety Certifications: UL & CSA Certified
In the American market, UL (USA) and CSA (Canada) certifications are key requirements for industrial equipment. Our welding machines undergo rigorous testing to ensure compliance with:
· Electrical safety standards (preventing short circuits, overloads, etc.)
· Fireproof and material compliance (meeting North American environmental regulations)
· EMC electromagnetic compatibility (avoiding interference with other equipment)
These certifications give customers peace of mind when purchasing, with no compliance concerns.
2. Voltage & Frequency Adaptation: 220V 60Hz for American Power Systems
The voltage standards in the Americas (e.g., USA, Canada, Mexico) differ from those in Asia and Europe. Our welding machines feature optimized circuitry to ensure:
✅ 220VAC 60Hz compatibility—perfectly matches the American power grid
✅ Wide voltage design—handles fluctuations, preventing equipment damage
✅ High energy efficiency—reduces electricity costs and boosts productivity3. Robust Packaging & Safe Shipping: Ensuring Damage-Free Delivery
International shipping can involve long sea or land journeys with rough handling. We use multi-layer protective packaging:
�� Internal cushioning—high-density foam + sponge for shock absorption
�� Reinforced exterior—custom wooden crates, waterproof and impact-resistant
�� Professional logistics partners—guarantee on-time, secure delivery4. Language Localization: English Interface & Local Language Support
To ensure ease of operation for American customers, we provide:
�� English operating interface (Spanish, French, etc. available)
�� English manuals & technical documentation (clear and easy to understand)
�� English tutorial videos (quick setup and operation)Eliminating language barriers improves productivity!
5. Rapid After-Sales Support: 1-Minute Engineer Response
Equipment failures can disrupt production, so we offer:
⚡ 1-minute response time—professional engineers on standby
�� Local spare parts inventory—minimizes downtime
�� Scheduled maintenance reminders—extends equipment lifespanWhy Choose Our Welding Machines?
✅ Fully compliant with American standards (UL/CSA certified)
✅ Optimized for local power supply (220V 60Hz)
✅ Secure packaging for safe transport (shockproof & waterproof)
✅ No language barriers (English interface + manuals)
✅ Hassle-free after-sales service (1-minute rapid response)Choose Us for the Best Welding Solution Tailored to the American Market!
�� Contact us now for a customized solution!
Get professional support now
Related product links
-
Apr 17,
2025Subject: Laser Welding Users' #5 Concern!After-sales service and technical support rank as the TOP5 concern for laser welding machine users.
Industry data reveals:
• 60%+ buyers prioritize after-sales support when selecting equipment (Laser Manufacturing News 2023)
• 35% of customers switch suppliers due to poor service (1,200-user survey)
Common pain points we solve:
⌛ 48+ hour response times from competitors → Our 24/7 live support
�� Days-long downtime → 48-hour spare parts delivery guarantee
��️ Untrained operators → Free certified training programsSuccess Case:
After an electric vehicle battery tray manufacturer started using our services:
✓ The response time to malfunctions was reduced by 85%.
✓ The comprehensive utilization rate of the equipment increased by 23%.
✓ The annual maintenance cost decreased by 18%.
This isn't just equipment - it's production insurance.
[Schedule a consultation] today to discuss your specific needs.
P.S. Stay tuned for "User Concern #4: Safety and Compliance" in our next insight.
Get professional support now
Related product links
-
Apr 14,
2025Common Methods of Mold Repair!Molds are of vital importance in industrial production. However, issues such as wear and cracks occur frequently. How should one choose the right welding repair technology? As a leading brand in the field of mold welding equipment, San Laser. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the most common mold repair welding methods and offer professional solutions.

1. Laser Welding: The First Choice for High-Precision Repair
Applicable Scenarios: Precision injection molds, die-casting molds, molds with high surface finish
Advantages:
✅ Ultra-high precision (error < 0.1mm), suitable for the repair of tiny cracks
✅ Small heat-affected zone, reducing the risk of mold deformation
✅ Compatible with automation, and can be used with robotic arms for batch repair0. Tungsten Inert Gas Welding (TIG): A Universal Welding Solution
Applicable Materials: Stainless steel, aluminum alloy, copper alloy, etc.
Advantages:
✅ High welding strength, suitable for molds that bear high stress
✅ Widely available equipment and relatively low operation threshold
✅ Capable of repairing large-area damage
Expert Tips:
• The preheating temperature needs to be strictly controlled (for example, H13 steel needs to be preheated to 300-500℃)
• Pulse TIG welding is recommended to reduce thermal deformation0. Cold Welding Technology: A Special Solution without Thermal Deformation
Applicable Scenarios:
• Thin-walled molds (such as electronic connector molds)
• Heat-treated molds (to avoid secondary annealing)
Advantages:
✅ Welding at room temperature, without thermal stress
✅ No need for subsequent processing, saving time
Disadvantages:
❌ The bonding strength is relatively low (about 60-70% of the base metal)
❌ Only suitable for the repair of non-stressed parts0. Other Emerging Technologies
4.1 Friction Welding
• Heat is generated through mechanical friction, suitable for the welding of dissimilar metals
• Typical case: Repair of mold inserts
4.2 Electron Beam Welding (EBW)
• Carried out in a vacuum environment, suitable for aerospace-grade molds
• Expensive equipment, limited to high-end fields0. Why Choose San Laser's Welding Equipment?
• Low operation difficulty: The optical path movement direction can be remotely controlled through a three-axis operating lever, saying goodbye to manual adjustment of the optical path.
• Proprietary technology: The split operation design allows you to frequently adjust parameters at a distance of up to 4 meters.
• Global service: Provide 24-hour remote technical support.The new mold repair welding machine of the 2025 model is now on hot sale. Come and experience the brand-new and ultra-precise mold repair experience!
Get professional support now
Related product links
-
 about san laser
about san laserA pioneer in the world of Laser technology for the last 10 years, proudly presents its latest laser machines for various applications.
Learn more -
 Application and Clent Stories
Application and Clent StoriesThe wide applications of these machines work on materials like Leather, Wood, Acrylic, Fabric and Paper processing industries.
Learn more